¶ NLP Prompt Context Injection Tool
For the source code, please see the GitHub page.
In the context of using language models or AI systems, injecting context into prompts could involve providing supplementary details or background information to improve the model's performance or guide it toward a more desired output. This could be done to make the model more context-aware and to influence its responses in a particular way.
In the terminology of large language models, prompt context injection is commonly called retrieval augmented generation (RAG) as stated in the original paper.
Prompt injection is a fine-tuning method for large language models, providing easy methods to inject context into the language model without explicit training of the model. Moreover, the limitied context window of the transformer based language models hinder using huge documents to be injected into the prompt - so the most applicable, semantically related parts (chunks) needs to be selected.
¶ Sentence (document) embedding
For selecting proper, semantically related documents for a prompt, a commonly used method is to embed the chunk into a high dimensional space, which enables to compute similarity metrics. For commonly available models of sentence embedding and similarity estimation, HuggingFace library provides a couple of solutions.
¶ Vector databases
Vector databases provides tools to store blobs indexed by high dimensional vectors. They helps to query the database based on the vectors by different metrics (like Euclidean, cosine distance) using exact (flat) and approximate searches. Vector databases can handle millions or billions of documents efficiently. Most prominent implementations of vector databases are
- MongoDB
- Milvus
- ChromaDB
- Azure CosmosDB
¶ Injection process
The common method of prompt context injection is depicted on the figure bellow.
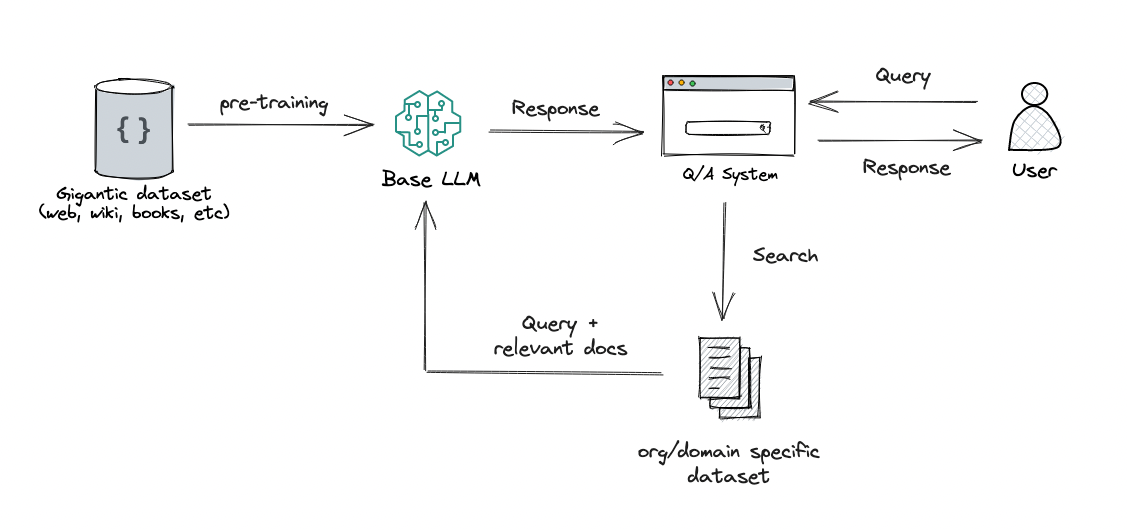
¶ Implementation
The implementation uses the MiniLM-L6-v2 model to embed chunks. The embeddings are stored in a MilvusDB, and embeddings similarity is based on cosine distance. populate.ipynb can be used to inject document into the vector database, while query.ipynb to query the database. query.ipynb is a deployable notebook.
The inputs for the service:
prompt: the input prompt (string)
The responses:
resp: the most similar documents (array of strings)
¶ Tutorial
...
¶ Best practices
¶ RAG is just a workaround
Please be aware, that RAG is just a workaround! Please see e.g. this entry.
¶ Selecting chunk size
It is very important to keep eye on the size of the chunks in the database. Using small chunks results in missing information in the context prompt, since nearby text around sentences can bear meaningful information to react a specific prompt. Big chunks however fill the context window of the LLM. Huge models, like GPT-4 has enermous context window (128K), but smaller models, like Falcon 7B has only 2048 sized window. So compromise between huge and small chunks is an issue, and depends on the use-case. Commonly, in a plain text, a chunk can be one or two sentence long, however, different applications might require bigger windows.
¶ Number of injected chunks
...
¶ Metrics and embedding models
...
¶ Injecting huge amount of data
...
¶ Selecting proper vector indices
..